The Most Secure of 3 Forms of Two/Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor, or two-factor, authentication is a security feature that helps protect users' accounts by requiring extra input when a user attempts to log into one of their accounts. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is allowed by the provider of the account, and there are different forms of MFA. Multi-factor authentication occurs after a user enters their account credentials which are comprised of a user ID and a password. Unfortunately, these credentials can often be hacked, which is why MFA was introduced. MFA can be accomplished in one of three common ways:
- SMS (Short Message Service) aka text
- Authenticator apps
This post discusses how multi-factor authentication helps protect your accounts, as well as the most secure of the three MFA forms.
The Most Secure of 3 Forms of Two/Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication adds a second step to logging into an account. After a user ID and password are entered, users are then prompted for a secondary code sent via SMS, email, or provided by an authenticator app. The idea behind MFA is that a user's credentials can be stolen, but requiring an additional security step should prevent access by the wrong person.
It is important to understand that no system is 100% full-proof or without its own risks. Even between the three types of multi-factor authentication, there are differences in the level of security provided. More specifically, using an authenticator app for MFA is the most secure way. It is also important to clarify that adding any available form of MFA is better than none at all.
SMS
Short message service, or SMS, multi-factor authentication works by sending a code via text to the phone number registered in the account each time the user attempts to log into their account. The user then enters the code into the prompt and as long as it matches what was sent, they are then logged into their account.
NOTE: The user must first enter the correct user ID and password to be sent an MFA code.
Some accounts will allow users to "remember a device". This means once they log into the account using a legitimate MFA token, they can then log into their account for a specific amount of time without being required to enter another MFA token. The time period allowed can span from a few days to 30 days, and varies by the account being logged into.
Unfortunately, SMS multi-factor authentication is not the most secure method of MFA. This form of MFA relies upon a user's phone number, which is tied to the SIM card in their phone. SIM cards can be compromised in several ways.
SIM cards can be cloned without a user knowing it, meaning another user can get copies of all of the same notifications. Another risk to SIM cards is having your number moved to a new phone without your consent. This process is known as a "SIM swap" and can be accomplished using social engineering or by hackers consolidating personal information exposed in data breaches to contact your phone company and convincing them they are the owner of the number.
There are additional attacks that can be made against SIM cards, which is the biggest reason it is not the most secure form of multi-factor authentication. Check out this article for more information about these as well as other attacks on SMS MFA.
Email is another form of multi-factor authentication. Accounts that support this will allow users to add an email account, which will then receive MFA tokens from the account provider when the user attempts to log into that specific account.
The main problem that can arise when using email for multi-factor authentication is that if you ever lose access to your email, or your email account is hacked, any accounts using it for MFA can be at risk. Sending email to a user locked out of an account is one of the most common account recovery options. This is why it is so critical not to lose control of email accounts tied to other user accounts. For more information on why you never want to reuse your email credentials, check out our previous post about this.
If someone else gains access to an email account you use to log into other accounts, they could easily access any MFA tokens sent to that email. This would allow someone else to log into your accounts, possibly change passwords and much more. This is why email is also not the most secure form of multi-factor authentication.
Authenticator app
Lastly, there are authenticator apps whose purpose is to provide multi-factor tokens for applications that have been configured on them. Authenticator apps are free, and there are a wide variety of them including ones from LastPass, Microsoft, Google just to name a few. An authenticator app typically has you scan a QR code to add an account to it.
Whichever authenticator app you use, one of the biggest benefits to them is that the MFA tokens they provide refresh every 30 seconds, making them extremely secure. Additionally, authenticator apps require you to sign in to them, much like a banking app, and because the tokens are only available via the app, they are by far the most secure multi-factor authentication method.
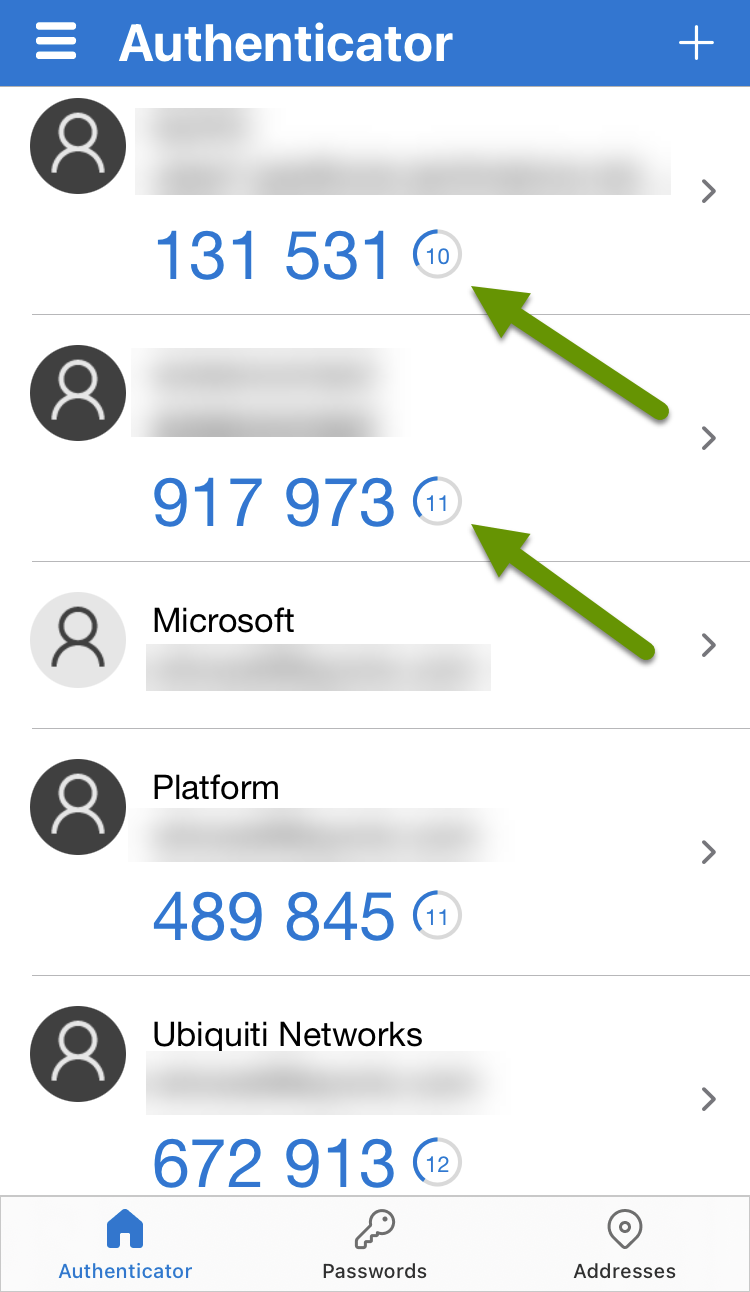
Using any of the three forms of multi-factor authentication is better than none, as it makes it one step harder for someone to gain access to one of your accounts, even if they have access to your account credentials. Using an authenticator app is a far more secure choice of MFA compared to SMS and email. Keep in mind most companies do not provide every type of MFA, so you will need to work with what they have available. When given the choice, your accounts will be kept more secure if you choose to use an authenticator app whenever available.
As always, there is more than one way to accomplish the same thing, but that does not mean they are all the same!

